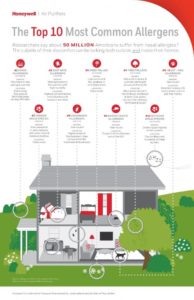
Airborne allergies are very common during springtime, but allergy sufferers have to stay alert all year round if they want to curb their symptoms.
When they hear about airborne allergies, most people mistakenly think of pollen allergy, but pollen is not the only allergen to cause problems.
Due to the high pollution level modern society faces while living in large cities, more and more people develop dust, mould, or pet dander allergies each year.
What Is An Allergy?
OK, we all heard about allergies. Some of us even suffer from allergies, but what are they exactly?
Allergies are specific reactions of the immune system to a normally harmless particle or substance, which would not bother most people. Allergy sufferers are often sensitive to more substances at the same time.
Here is a list of the substances which are more likely to cause an allergic reaction.
- Pollen
- Mold
- Dust Mites
- Pet Dander
- Medicines
- Insect Venom
- Food
- Latex Rubber
What Is An Allergic Reaction?
The body’s immune system acts as a defense against invading germs like viruses or bacteria. However, in most allergic reactions the immune system responds to a false alarm.
When a sensitive person first comes in contact a specific allergen, the immune system will treat it as an invader and it will prepare its attack.
The immune system prepares its attack by generating large amounts of antibodies called immunoglobulin E or IgE. Each IgE is specific for a single substance.
If a person suffers from pollen allergy, the immune system will use different antibodies for each type of pollen. For example, the immune system will produce a different type of antibody when it has to face elm pollen than the one used for oak pollen.
IgE molecules are the only type of antibody that is able to attach tightly to mast cells, which are a type of tissue cells, and to basophils which are a type of blood cell. When an allergen will encounter a sensitive IgE molecule, it attaches to it like a key sliding into a lock.
This action notifies the cell on which the IgE molecule is attached to produce (in some cases) and release powerful chemicals like histamine which determines inflammation. These chemicals are able to act on different tissues, like those in the respiratory system, and cause various symptoms.
Symptoms Of Airborne Allergies
People who first experience an airborne allergy might believe they suffer from the cold. The most common symptoms include, but are not limited to:
- Sneezing – most often accompanied by a runny or clogged nose.
- Itching eyes, throat, and nose
- Watering eyes
- Coughing and postnasal drip
- Conjunctivitis
- Allergic salute – this sign is usually noticed in children. A crease mark appears on the nose after persistent upper rubbing
- Allergic shiners – dark circles appear under the eyes because of the increased blood flow near the sinuses.
When an allergen is inhaled by a person who is not allergic, the mucus in the nasal passages will simply move the foreign particle to the throat where it may be swallowed or coughed out.
However, something different happens when a sensitive person inhales the airborne allergen.
As soon as the allergen is inhaled by a sensitive person, it lands on the lining inside the nose. This leads to a chain reaction that determines the mast cells in these tissues to release chemicals, among them histamine.
The chemicals contract certain cells in the lining of small blood vessels in the nose. The contraction allows fluids to escape, causing the nasal passages to swell. The result is a nasal congestion.
Histamine can also cause sneezing, irritation, itching, and excess mucus production, which might lead to an allergic rhinitis.
Mast cells also release other chemicals, including leukotrienes and cytokines which also contribute to the allergic symptoms.
In some cases, people with allergies develop asthma, which can be a very serious condition, especially if it’s left untreated. The symptoms of asthma include, but are not limited to
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
The shortness of breath asthma sufferers experience is due to excess mucus production, a narrowing of the airways in the lungs, and inflammation. Asthma can be disabling and sometimes even fatal, so it shouldn’t be left untreated.
If a wheezing or a shortness of breath accompany your allergy symptoms, that is usually a sign that the airways are also involved in the allergic process, and you should consult a physician.

Allergy suffers must ensure that their dehumidifier contains an anti-bacterial filter and an ioniser
How To Differentiate Between A Cold And An Allergy
It’s very difficult to differentiate between a common cold and an allergy.
Both illnesses might present themselves with symptoms of coughing, runny nose, and sneezing.
However, allergy symptoms may last longer than a cold’s. If you experience respiratory illness symptoms for more than a week or two, you should consult a physician.
Why Do Allergies Affect Some People?
Scientists believe there is an inherited tendency to be allergic. People whose parents are allergic are more likely to develop allergies themselves. However, they do not inherit the tendency to be allergic to a specific allergen.
Children whose both parents are allergic are more likely to develop allergies than those with only one allergic parent.
Exposure to allergens when the immune system is already under stress and the body’s defenses are weakened, such as after a viral infection, seem to contribute to an allergy development.
Pollen Allergy
Tiny pollen grains are released from grasses, weeds, flowers, and trees starting with spring, though summer and even in autumn. These grains are carried over long distances by currents of air.
Although the role of pollen is to fertilize other plants, many of the grains released never reach their targets. Instead, these grains find themselves entering human noses and throats where they can trigger a seasonal allergic rhinitis called hay fever. This is actually pollen allergy.
Pollen is one of the most common particles that can cause an allergy. Unlike the other allergy-inducing particles, pollen is rather hard to avoid.
Foods, medicines, or animals that cause allergies can be avoided easily most of the times. Even insects and dust are escapable, but when the pollen count is high not even staying indoors with the windows closed will help you to avoid it.
What Is Pollen?
Plants produce round or oval pollen grains in order to reproduce. These grains are so small, they are impossible to see with the naked eye.
In some species, the pollen grains from one flower of a plant have to be carried by air currents to another plant of the same species to reproduce.
In other species, insects ensure the transport of pollen grain from one plant to another. A smaller number of plants use the pollen they produce to fertilize itself.
The types of pollen usually involved in allergies are produced by plain-looking plants, such as trees, weeds, or grasses that don’t have beautiful or large flowers. These plants produce a small, light, and dry type of pollen that is easily transported by the air currents.
In a recent study, scientists have collected ragweed pollen samples 400 miles out at sea, and even 2 miles high in the air. Because airborne pollen is light, it can travel long distances, so it’s usually useless to eliminate an offending plant from a specific area.
In addition, most plants that produce airborne pollen do it in huge quantities. A single ragweed plant can generate up to one million grains of pollen in a single day.
The main factor that determines if a pollen grain is more likely to cause hay fever is the type of allergens it contains.
For example, pine trees produce large amounts of pollen each day, so they would be good candidates for allergy causes. However, allergies are rarely caused by pine tree pollen because the type of allergens present in it seem to be less allergenic than the ones produced by other species of trees.
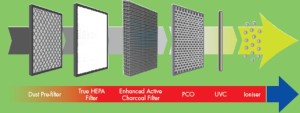
A multi-filtration system works by removing larger particles first before removing smaller particles. This system results in healthier air.
In addition, the grains of pine pollen are heavy so they are more likely to fall straight down from the tree without being carried by the air currents and reaching human noses.
Weeds are usually the most prolific allergenic pollen producers in an area, but grasses and trees are also important sources of allergens.
It’s more common to hear people say they are allergic to flower pollen, but that’s usually not true. People who complain they are allergic to roses, orchids, or other scented flowers are usually allergic to other types of pollen, as well.
Only people who have prolonged contact with this type of flowers will develop allergies to their specific pollen because the pollen grains are heavy and it’s carried by insects rather than air currents.
When Do Plants Make Pollen?
Pollen allergy is seasonal by nature because people will only present symptoms when the pollen grains to which they are sensitive are in the air. As each plant has a pollinating period that is more or less the same each year, most people will only present allergy symptoms in that year period alone.
Weather conditions play a major role in affecting the amount of pollen produced and distributed each year. In the Northern Hemisphere, the pollinating season starts later the farther north you go. Pollen counts also tend to be higher on dry breezy days than on chilly wet ones.
Mould Allergy
There are several thousands of mould and yeasts types in the fungus family. Yeasts are single cell organisms that divide to form larger clusters.
Moulds are multiple cell organisms that grow as branching threads or hyphae. Although both yeasts and molds can cause allergic reactions, only a reduced number of moulds are common allergens.
Spores are the reproductive pieces of fungi. They differ in shape, size, and color for each type of mould. When a spore germinates, it can give rise to a new mould, which can, in turn, produce more spores.
What Is Mould Allergy?
Mould allergy is usually caused by the inhalation of fungal spores, or sometimes even of pieces of fungi. This can cause an allergic rhinitis. Because of their small dimensions, some mould spores can even reach the lungs.
A small number of people can also develop or worsen their mould allergy by eating foods that have been processed with fungi. On occasion, foods containing yeast can also produce allergy symptoms.
Where Does Mould Grow?
Mould can grow on most surfaces if it finds the proper conditions. In order to grow, mould has to have moisture, oxygen, and a source that can provide some other chemicals.
You can usually see mould growths in the autumn, when they will grow on logs, leaves, grasses, or weeds, usually in shady, moist areas.
You can also find mould growth inside your home. Mould will usually grow in damp spaces, like bathrooms (especially in shower stalls), basements, closets, in appliances like air conditioners and humidifiers, and in mattresses, or behind the furniture.
Mould especially likes growing in bakeries, barns, breweries, and greenhouses. Mill workers, carpenters, and furniture repairers are more likely to work in mouldy environments.
Mould spores are airborne allergens only if there are numerous and they are light enough to be carried by air currents. The type of spore is also very important because only a few dozen mould species are considered significant allergens.
Other Mould-Related Disorders
Fungi may cause other heath problems, besides allergic diseases. Some kinds of Aspergillus may cause both infections and allergies. The fungi can lodge in the airways or even in the lung and grow into a sphere known as a fungus ball. When the immune system is stressed and the body’s defenses are down, Aspergillus may invade the lungs or the whole body.
Exposure to some of these fungi can lead to asthma or a severe inflammatory disease called allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. This latter condition is serious, but it only affects a small number of people.
House Dust Allergy
People who suffer from dust allergy are actually allergic to dust mites. These microscopic organisms live in the dust found everywhere, in households or workplaces.
House dust contains microscopic mites that are the most common cause of perennial allergic rhinitis. This airborne allergy usually produces similar symptoms to pollen allergy, but it can also produce asthma.
House dust mites live in bedding, carpets, and upholstered furniture. They thrive during the summer and die in the winter. However, they continue to thrive even in the winter in a warm and humid environment.
The particles of dust you can see floating in a shaft of sunlight contain dead dust mites and the waste they produce, as well. The waste produced by the mites are proteins, and they are actually the ones provoking an allergic reaction.
Other Allergens Found In House Dust
House dust contains many other allergens other than dust mites, even though they are the most common allergy-inducing particles. Here is a list of the other allergens your house dust might contain.
- Bacteria
- Food particles
- Feathers, cotton lint, or other stuffing materials
- Pet dander
- Bits of insects and plants
Cockroaches can also be found in crowded cities. Their feces and saliva contain protein that can also be found in your house dust. This protein can cause allergic reactions, especially in children.
Animal Allergy
Many people believe they are allergic to the fur of cats or dogs. Studies have shown, however, that the major allergens produced by pets are actually proteins contained by their saliva. These proteins stick to the pet’s fur when it cleans itself.
Another major source of allergy-causing protein is the urine. While this might not be a problem for cat or dog owners, it might be for gerbil, rats, or mice owners.
Animal allergies usually take more than 2 years to develop, and some people might present symptoms for more than 6 months after the exposure.
Carpets and upholstered furniture are reservoirs for pet allergens, and they can maintain them in the air for months after the animal has been removed.
Chemical Allergies
Some people might report allergies to different chemical substances in their environment. These substances can be found in
- Cigarette smoke
- Paints
- Perfumes
- Plastics
Even though the symptoms may resemble those in an allergy, recent studies have shown that these reactions are not caused by a real allergen. In fact, these are reactions to a chemical irritant, but it may affect allergy sufferers more than others.
How To Prevent Allergy Development
Mould and Pollen
It’s very difficult to completely avoid exposure to pollen. Even if you remove the plant responsible for your allergy from your environment, the airborne pollen grains can travel for hundred of miles.
You can avoid exposure to mold if you constantly clean the damp areas in your home with a mould-repellent substance. Using a dehumidifier will also help.
In order to reduce exposure to pollen:
- Stay indoors with the windows closed in the mornings when the pollen levels are higher.
- Wear a specially designed anti-pollen mask when outdoors.
- Choose your vacation period when the exposure would be minimal
House Dust And Pet Hair
If you suffer from dust or pet hair allergy, this is how you can reduce the exposure:
- Use a vacuum cleaner with a good HEPA filter
- Wear a face mask when you’re cleaning the house
- Use high-quality air filters for your air conditioner and change them as often as the manufacturer recommends.
- Try to remove large carpets, as they trap a lot of dust
Do you suffer from airborne allergies? Let us know how they affect you in the comments below.